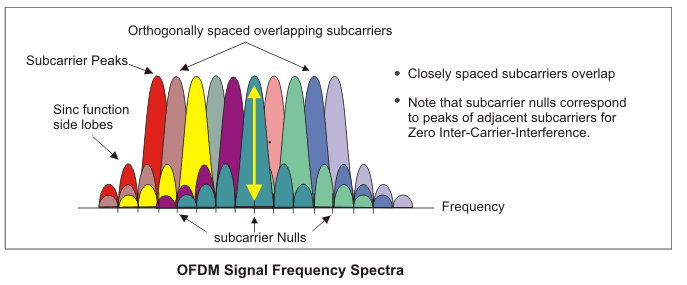
In this research project the method of multicarrier transmission is to be implemented and tested in practice. The best-known multicarrier method is Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) and is used in many current standards such as LTE, WLAN, 5G, to name only the most important ones.
OFDM is very powerful with long echo runtimes of the signals, easy to implement by means of FFT, but it also has some serious disadvantages. Among these are the moderate spectral efficiency and the high demands on the linearity of the transmitter.
These disadvantages lead to an out-of-band radiation, which can interfere with adjacent channels. To reduce this out-of-band radiation, variants of OFDM have been proposed in the literature which are known as Filter Bank Modulation Carriers (FBMC).